Gum Cancer – A Growing Concern
A cancer diagnosis, no matter where it occurs, is a life-altering moment. When it involves the gums, it often goes unnoticed until it disrupts everyday activities, such as eating or speaking. Gum cancer, a type of oral cancer, may seem less talked about, but it carries serious implications if ignored.

Globally, oral cancers account for nearly 3% of all cancer cases, with gum cancers forming a significant subset. According to the World Health Organization, oral cancers claim over 177,000 lives annually. In India, oral cancers, including those of the gums, make up almost 30% of all cancer cases, mainly due to high tobacco usage and poor oral hygiene.
“Early detection is crucial in gum cancer. Unlike other head and neck cancers, gum malignancies are frequently mistaken for benign conditions like gingivitis or ulcers,” explains Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a distinguished surgical oncologist based in Bangalore. “Timely recognition, followed by expert intervention, significantly improves outcomes for patients.”
What is Gum Cancer?
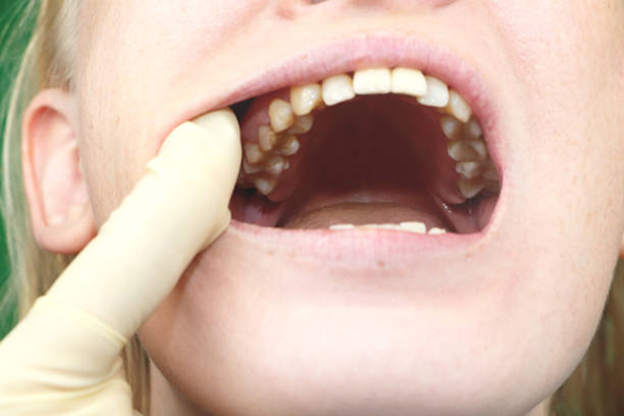
Gum cancer often begins subtly, and early changes in the gums can be mistaken for common irritation or infection. Gum cancer, also known as gingival cancer, originates in the squamous cells lining the gum tissue. It usually affects the lower gums, but can appear in the upper gums as well. It’s categorized under oral cavity cancers and often manifests as lesions that refuse to heal.
Gum cancers typically fall under the category of squamous cell carcinomas, which represent over 90% of all oral cancers. Rarely, minor salivary gland tumors or melanomas may also affect the gums. While gum cancer can affect anyone, it’s more prevalent among:
- People over the age of 40
- Chronic tobacco users
- Individuals with poor dental hygiene
- Those exposed to Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Gum Cancer Symptoms and Causes

“In the early stages, gum cancer may appear as an innocuous swelling or sore. However, these changes are persistent, painless initially, and resistant to regular treatment,” says Dr. Athira Ramakrishnan, a seasoned oral cancer specialist based in Bangalore. “This delay in seeking medical help allows the cancer to advance silently.”
Root causes behind gum cancer:
Need Assistance?
Worried about unusual gum changes that don’t seem to heal? A comprehensive evaluation by an oral health expert can help clarify your next steps.
Diagnosis and Tests
Catching gum cancer early increases the likelihood of a full recovery. Diagnosis often begins with a clinical oral examination and progresses through a series of advanced imaging and tissue studies.
Key Diagnostic Tools:
Physical Examination: A thorough evaluation of oral tissues to detect abnormal growths.
Biopsy: A small tissue sample is taken from the suspicious lesion to confirm cancer.
Imaging Tests:
- CT scans and MRI to evaluate the spread
- PET scans to detect distant metastasis
- Endoscopy, if there’s suspicion of spread to nearby regions like the throat or nasal cavity
According to the MACS Cancer specialists, “Accurate staging of gum cancer is vital for tailoring treatment. A comprehensive diagnostic approach ensures that no microscopic detail is missed, ultimately guiding better treatment decisions.”
Gum Cancer Stages
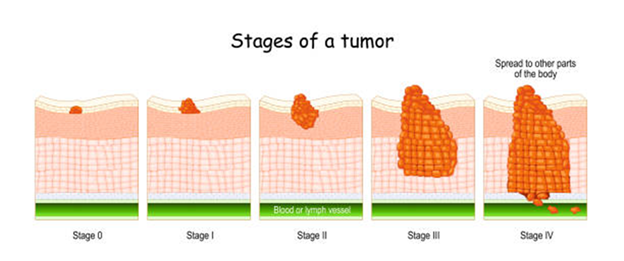
Stage I: Tumor is 2 cm or less in diameter and does not involve lymph nodes.
Stage II: Tumor is between 2–4 cm, no lymph node spread.
Stage III: Tumor may be larger or involve nearby lymph nodes.
Stage IV: Cancer has spread to deeper tissues, lymph nodes, or distant organs.
“The stage at which gum cancer is diagnosed heavily impacts survival rates. For instance, Stage I has a 5-year survival rate of over 80%, while Stage IV drops below 40%,” explains Dr. Abhilasha Sadhoo, an accomplished ENT and Head and Neck Oncosurgeon in Bangalore. “That’s why routine dental check-ups and prompt evaluations of suspicious lesions are critical.”
Need Assistance?
Unsure how advanced your symptoms are? Early assessment by a specialist can provide clarity and guide you toward the most appropriate care.
Management and Treatment Options for Gum Cancer
Surgery
Surgical removal is often the first choice, especially in the early stages. This may involve:
Tumor excision
Partial jawbone removal (mandibulectomy) in advanced cases
Radiation Therapy
High-energy beams are used to target and destroy cancer cells. It may be used:
- As a primary treatment
- Post-surgery to kill residual cancer cells
Chemotherapy
Used in combination with radiation or for advanced/metastatic cancers.
Targeted Therapy & Immunotherapy
Advanced options for specific genetic mutations or immune responses in cancer cells.
“Successful gum cancer treatment doesn’t stop with surgery or radiation. Rehabilitation, including physical therapy and emotional support, plays a vital role in restoring quality of life,” says Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a compassionate oncological surgeon based in Bangalore.
Prevention
FAQs
1. How curable is gum cancer?
2. Can you recover from mouth cancer?
3. How long do oral cancer patients live?
4. Are all gum lumps cancerous?
5. What’s the difference between gum disease and gum cancer?
Need Assistance?
Are you noticing unhealed sores or changes in your gum tissue? Consult a qualified oral cancer specialist to assess your symptoms and explore suitable treatment pathways.
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only. Individual results may vary. Please consult a qualified doctor for personalized advice
