Hurthle Cell Carcinoma
This page covers the management of Hurthle Cell Carcinoma, a rare and aggressive thyroid cancer. It details the latest diagnostic and treatment methods for this challenging condition, developed with insights from MACS Clinic and Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a world-renowned surgical oncologist in Bangalore, India, known for creating the RABIT technique for robotic thyroidectomy.
What is hurthle cell carcinoma?
Hurthle Cell Carcinoma is a rare and aggressive type of thyroid cancer that originates from Hurthle cells, which are a variant of the follicular cells in the thyroid gland. These cells are larger and contain more mitochondria, making the cancer more challenging to diagnose and treat. Hurthle cell carcinoma has a higher potential for spreading to lymph nodes and distant organs compared to other thyroid cancers.
Dr. Sandeep Nayak an experienced surgical oncologist in India, explains, “Hurthle cell carcinoma presents unique challenges, requiring a meticulous and personalized treatment approach that leverages the latest advancements in surgical and medical care.”
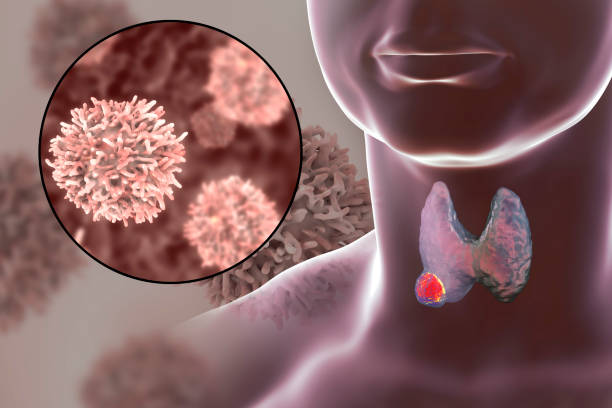
Moving forward, let’s dive into what you need to know about Hurthle cell carcinoma.
Symptoms of Hurthle cell carcinoma
 Hurthle cell cancer often presents with symptoms that are similar to other types of thyroid cancer, including:
Hurthle cell cancer often presents with symptoms that are similar to other types of thyroid cancer, including:
- A lump in the neck
- Difficulty swallowing
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Neck pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
Causes of Hurthle Cell Carcinoma
The exact cause of Hurthle cell thyroid cancer is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Genetic mutations: Alterations in the genes responsible for cell growth and division can lead to the development of Hurthle cell cancer.
- Radiation exposure: Previous exposure to radiation, especially to the head and neck, increases the risk of developing thyroid cancers, including Hurthle cell carcinoma.
- Iodine deficiency: A diet low in iodine, essential for thyroid function, can contribute to the development of thyroid cancers.
- Family history: A family history of thyroid or other endocrine cancers may increase the risk.
- Age and gender: Hurthle cell carcinoma is more common in older adults and tends to affect women more frequently than men.
Have a Question?
Early detection is crucial for managing Hurthle cell carcinoma. If you have concerns about thyroid health, consult a medical professional today.
Now, let’s explore how fast Hurthle cell cancer can develop.
How fast does Hurthle cell cancer grow?
Hurthle cell carcinoma usually grows more slowly compared to some other aggressive cancers. However, this can vary significantly from person to person.
Factors influencing the growth rate include:
- Stage of the cancer: Early-stage Hurthle cell carcinoma may grow more slowly, while advanced stages can progress more quickly.
- Extent of spread: The rate at which it grows can be affected by whether it has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
- Individual patient health: Overall health and individual biological factors can influence how quickly the cancer grows.
Although Hurthle cell cancer generally grows more slowly, it has a higher likelihood of recurring or spreading compared to other thyroid cancers. Early detection and management are crucial for improving outcomes.
Wondering about your prognosis? Let’s take a closer look at the survival rate of Hurthle cell carcinoma.
What is the survival rate of Hurthle cell carcinoma?
Hurthle cell carcinoma generally has a good prognosis, particularly when detected early.
Overall, survival rates for Hurthle cell cancer are similar to, or slightly lower than, those for follicular carcinoma thyroid cancer.
- Early-stage cancers: Survival rates for early-stage Hurthle cell carcinoma are often excellent, frequently exceeding 95% at 5 years.
- Influencing factors: The stage of cancer, presence of lymph node or distant metastases, and patient age can all impact the outcome.
Ready to understand how it’s classified? Let’s break down how Hurthle cell cancer is staged.
How is Hurthle cell cancer staged?
Hurthle cell carcinoma is staged using a modified version of the TNM system, which considers three key factors:
- T (Tumor): Describes the size and extent of the primary tumor.
- N (Nodes): Indicates whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- M (Metastasis): Determines if the cancer has spread to distant organs.
Unique aspects of Hurthle cell cancer staging:
- Age: Patients under 55 are often classified as having a lower stage, even if they have larger tumors or lymph node involvement.
- Differentiation: The appearance of the cancer cells under a microscope is taken into account, influencing the staging and treatment approach.
This modified staging approach helps in tailoring treatment and predicting outcomes for Hurthle cell carcinoma.
Discover how Hurthle cell cancer is diagnosed.
Diagnosing Hurthle cell cancer
Physical examination: Your doctor will check for lumps or swelling in your neck.
Blood tests: These help assess thyroid function and rule out other conditions.
Imaging tests:
- Ultrasound:Visualizes the thyroid gland and any nodules.
- CT or MRI:Provides detailed images of the thyroid and surrounding areas.
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy: A thin needle is used to extract cells from the thyroid nodule for examination under a microscope. This is often crucial for confirming the diagnosis.
Pathology examination: A pathologist examines the biopsy sample to determine the type of cells present and whether they are cancerous.
If Hurthle cell carcinoma is suspected, further tests may be needed to determine the stage of the cancer, such as:
Chest X-ray
Bone scan
PET scan
These additional tests help assess if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment for Hurthle cell carcinoma
Treatment for Hurthle cell thyroid cancer therapy depends on the stage and extent of the cancer. Common treatment options include:
Surgery:
- Thyroidectomy: The primary approach for Hurthle cell carcinoma is the surgical removal of the thyroid gland. At MACS Clinic, we use the revolutionary Robotic-Assisted Breast-Axillo Insufflation Thyroidectomy (RABIT) technique. Developed by Dr. Sandeep Nayak, RABIT employs the Da Vinci robotic system to perform the procedure through small, discreet incisions in the armpit. This method provides enhanced precision, magnification, and 3D vision, leading to superior surgical results and minimal scarring.
- Lymph node dissection: If the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, they are removed during surgery. This helps to ensure that any cancerous cells in the lymphatic system are addressed, reducing the risk of recurrence and improving overall treatment effectiveness.
- Radioactive iodine therapy: After surgery, radioactive iodine therapy may be used to target any remaining cancer cells. This treatment is particularly effective for certain types of thyroid cancer, though its use can vary based on the individual case.
Other treatments for incurable cancer:
Chemotherapy: Rarely used for Hurthle cell carcinoma, but may be considered in advanced cases or if the cancer is resistant to other treatments.
Hormone therapy: Suppressing thyroid hormone production can help control cancer growth.
Targeted therapy: Potentially available through clinical trials for personalized treatment approaches.
Dr. Sandeep Nayak emphasizes, “Advanced surgical modalities, such as robotic-assisted techniques, offer unparalleled precision and minimal invasiveness. These innovations not only enhance surgical outcomes but also significantly improve patient recovery times and reduce postoperative complications.”
At MACS Clinic in Bangalore, we are committed to offering comprehensive treatment for a wide range of head and neck cancers, including follicular carcinoma, papillary carcinoma, small cell carcinoma, and more. Utilizing the most advanced surgical options, such as endoscopy, robotic, and laparoscopic techniques, we ensure our patients receive the highest standard of care tailored to their specific needs.
Have a Question?
Learn more about cutting-edge treatments and innovative surgical techniques for Hurthle cell carcinoma. Get in touch today with an expert oncologist to discover how these advanced options can benefit your care.
Summary
Hurthle cell carcinoma, though rare, poses significant challenges due to its aggressive nature. Effective treatment often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including advanced surgical techniques. Early detection and tailored treatment are crucial for improving outcomes and reducing the risk of recurrence. By utilizing cutting-edge technologies and personalized care strategies, patients have a better chance of achieving positive long-term results.
Support
Each year, patients worldwide choose MACS Clinic for their care. Leveraging our extensive experience, we have simplified the process, allowing you to visit Bangalore for evaluations, scans, biopsies, and surgery in a single trip. Much of the follow-up can be managed through online consultations to further enhance your convenience. Additionally, we are dedicated to coordinating your postoperative treatment in your home country or city, so there is no need for you to return to Bangalore.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between follicular and Hurthle cell carcinoma?
Follicular carcinoma and Hurthle cell carcinoma are both thyroid cancers but differ in key ways:
- Cell type: Follicular carcinoma arises from follicular cells, while Hurthle cell carcinoma originates from Hurthle cells, a specific type of follicular cell.
- Aggressiveness: Hurthle cell carcinoma is more aggressive, with a higher risk of spread and recurrence.
- Treatment: Both are treated with surgery, but Hurthle cell carcinoma may need additional therapies due to its aggressiveness.
How does this condition affect the body?
Hurthle cell carcinoma can cause tumors in the thyroid, potentially affecting your ability to speak, swallow, and breathe. If left untreated, it may spread to other parts of the body, like the lungs and bones.
What is the recurrence rate of Hurthle cell carcinoma?
The recurrence rate of Hurthle cell carcinoma varies, but studies suggest it can be as high as 20-30%. The risk is influenced by factors such as the cancer’s stage, grade, and response to initial treatment.