Floor of Mouth Cancer
What is Floor of Mouth Cancer?
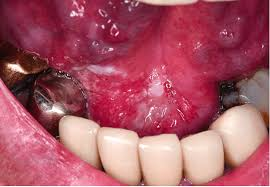
Floor of mouth cancer are cancerous tumors that arise within the soft tissues of the bottom of the tongue. This particular area is of vital importance in speech, swallowing, and salivation; thus, any cancer that arises here can be dramatically life-altering.
Dr. Sandeep Nayak, renowned for comprehensive head and neck surgery, says:
“Floor of mouth cancer most often is a squamous cell carcinoma, developing in the thin, flat cells that cover the interior of the mouth. It may invade neighboring tissues, lymph nodes, or other organs if not treated in its early phases.”
Early detection of oral cancers can significantly contribute to the success of the treatment. Advances in surgical techniques enable us to remove the tumors with the least loss of function and quality of life.”
Floor of Mouth Cancer – Symptoms
Swelling or lump under the tongue
As such symptoms might be mistaken for manifestations of lesser illnesses, medical attention is very important if the symptoms last longer than two weeks.
Need Assistance?
Have you noticed any recurring symptoms? It is recommended to consult a specialist early for an early diagnosis and proper treatment.
Floor of Mouth Cancer – Causes and Risk Factors
The human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly HPV-16, has been recognized as a significant risk factor for most oral cancers.

Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a seasoned surgical oncologist in Bangalore, underscores the following:
“Knowing the underlying reasons behind this condition can assist in making well-informed decisions. Lifestyle modification and education can lower the prevalence of oral cancers. Abstinence from tobacco, alcohol moderation, and good oral hygiene are the most important preventive factors.”
Types of Floor of Mouth Cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Most common form, originating from the thin, flat cells that cover the mouth.
Sarcomas
Tumors that develop in connective tissue like muscle, fat, or nerves.
Adenocarcinoma
An infrequent form occurring in the glandular cells for saliva production.
Melanoma
An aggressive but rare type of cancer that develops from pigment cells.
Floor of Mouth Cancer – Diagnosis
Management and Treatment of Floor of Mouth Cancer
Surgery
- In the case of early cancers, surgery is performed to remove tumors while maintaining function.
- In very advanced cases where the cancer has invaded a large area, removal of part of the jawbone (mandibulectomy) might be necessary.
- Reconstructive surgery involves tissue grafts or prostheses to rebuild the jaw and restore function and appearance.
Radiation Therapy
High-energy beams kill cancer cells:
- either as the main treatment for smaller tumors
- or following surgery to destroy any remaining cancerous tissue.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy employs strong drugs to kill cancer cells or inhibit their growth. It is usually employed in later stages or along with radiation therapy for enhanced efficacy.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted medications target specific molecules responsible for cancer growth, reducing harm to normal cells. The treatment is usually given in combination with other options.
Immunotherapy
This treatment enhances the patient’s immune system to identify and target cancer cells. It works best for cancers that recur or are in advanced stages and are not easily treated with other options.
According to the highly-skilled MACS Oncologist Team:
“The technology involved in minimally invasive surgery, such as robotic surgery, allows for more accurate removal of cancers and easier and quicker recovery. In advanced cases, reconstruction is crucial in restoring both function and aesthetics, significantly improving a patient’s quality of life.”
Need Assistance?
Worried about treatment? Talk to an expert to find the best solution for your condition.
Floor of Mouth Cancer – Stages
Stage 0 (Carcinoma in Situ) – The cancer exists only in the top layer of cells.
Stage 1 & 2 – Tumors are small and localized in the mouth.
Stage 3 – The tumor has grown in size and can have spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Stage 4 – Cancer is characterized by its presence in distant tissues or organs.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Brush teeth regularly and visit the dentist frequently.
FAQs
What are the primary symptoms of floor of mouth cancer?
Early symptoms are:
- persistent ulcers
- red or white patches
- swelling under the tongue
- unexplained pain
If any of these last more than two weeks, see a doctor.
What is the outlook for floor of the mouth cancer?
Is surgery always required for floor of mouth cancer treatment?
Is floor of mouth cancer able to metastasize to other body areas?
What lifestyle modifications can help prevent floor of mouth cancer?
Lifestyle modifications to help decrease floor of mouth cancer include:
- Prevention of tobacco use
- Limiting alcohol intake
- Good oral hygiene
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only and not for promotional use.
