Overview of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer is a critical health concern affecting thousands of people worldwide. This type of cancer, often beginning in the cells of the mouth or throat, can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated early. With advancements in diagnosis and treatment, the prognosis for many patients has significantly improved. This page provides an in-depth look at oral cancer, its symptoms, risk factors, stages, and the available treatment options, developed in conjunction with MACS Clinic and Dr. Sandeep Nayak. Dr. Nayak, a renowned expert in head and neck cancers, operates from Bangalore, India, and has pioneered several innovative surgical techniques in cancer treatment.
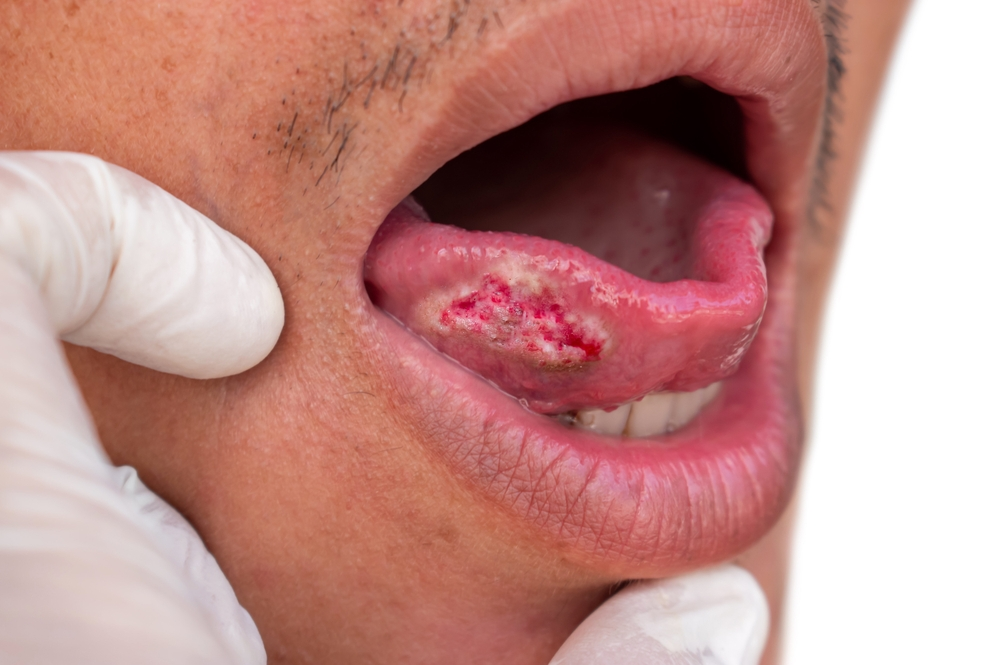
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer refers to cancer that develops in any part of the mouth, including the lips, gums, tongue, inner lining of the cheeks, roof of the mouth, or the floor of the mouth. The majority of oral cancers are squamous cell carcinomas, which tend to spread quickly if not treated.
Risk factors such as tobacco use, heavy alcohol consumption, and HPV infection have been linked to the development of oral cancer. Early detection is critical for successful treatment outcomes, emphasising the importance of regular dental checkups and awareness of symptoms.

Have a Question?
Early detection is crucial for managing oral cancer. If you have concerns about your health, consult a medical professional today.
Early Signs of Oral Cancer
Recognizing the early signs of oral cancer is essential for early diagnosis and better treatment outcomes. Some of the initial signs include:
Red or white patches on the gums, tongue, or lining of the mouth
A lump in the neck or mouth area
Unexplained bleeding in the mouth
Pain or difficulty swallowing
These signs may seem minor but should not be ignored, especially if they persist for more than two weeks. A biopsy is often required to confirm whether these signs are cancerous.
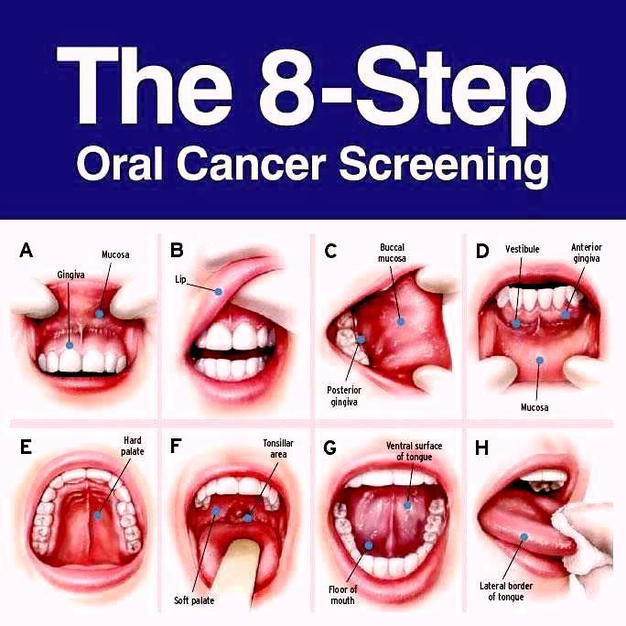
Symptoms of Oral Cancer
Recognizing the early signs of oral cancer is essential for early diagnosis and better treatment outcomes. Some of the initial signs include:
Pain in the mouth or ear
Unexplained weight loss
Loose teeth or dentures that no longer fit properly
Difficulty speaking, swallowing, or moving the jaw
Numbness in the tongue or other parts of the mouth
A sore throat that doesn’t go away
Prompt medical attention is vital for anyone experiencing these symptoms. Early-stage oral cancer has a higher survival rate, highlighting the importance of timely intervention.
Have a Question?
Learn more about cutting-edge treatments and innovative surgical techniques for oral cancer. Get in touch today with an expert oncologist to discover how these advanced options can benefit your care.
Causes and Risk Factors of Oral Cancer
Several factors increase the risk of developing oral cancer. These include:
Tobacco use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and using smokeless tobacco are significant risk factors for oral cancer.
Alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol use can contribute to the development of oral cancer, especially when combined with smoking.
HPV infection: Human papillomavirus, particularly strain HPV-16, has been associated with cancers of the oropharynx.

Sun exposure: Prolonged exposure to the sun increases the risk of cancer on the lips.
Age: The risk of oral cancer increases with age, with most cases occurring in people over 50.
Understanding these risk factors is essential for prevention and early detection.
Stages of Oral Cancer
Oral cancer is staged based on the tumour’s size and whether it has spread to nearby tissues, lymph nodes, or other parts of the body. The stages of oral cancer include:
Stage 0 (Carcinoma in situ): Abnormal cells are found in the lining of the mouth but haven’t spread.
Stage II: The tumour is 2-4 cm but still hasn’t spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage IV: The cancer has spread to nearby tissues, more lymph nodes, or distant parts of the body.
Stage I: The tumour is small, less than 2 cm, and hasn’t spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Stage III: The tumour is larger than 4 cm or has spread to one lymph node but not to distant organs.
Have a Question?
Early detection is crucial for managing oral cancer. If you have concerns about your health, consult a medical professional today.
Treatment Options
Oral cancer treatment depends on the stage and location of the tumour. Options include:
Surgery
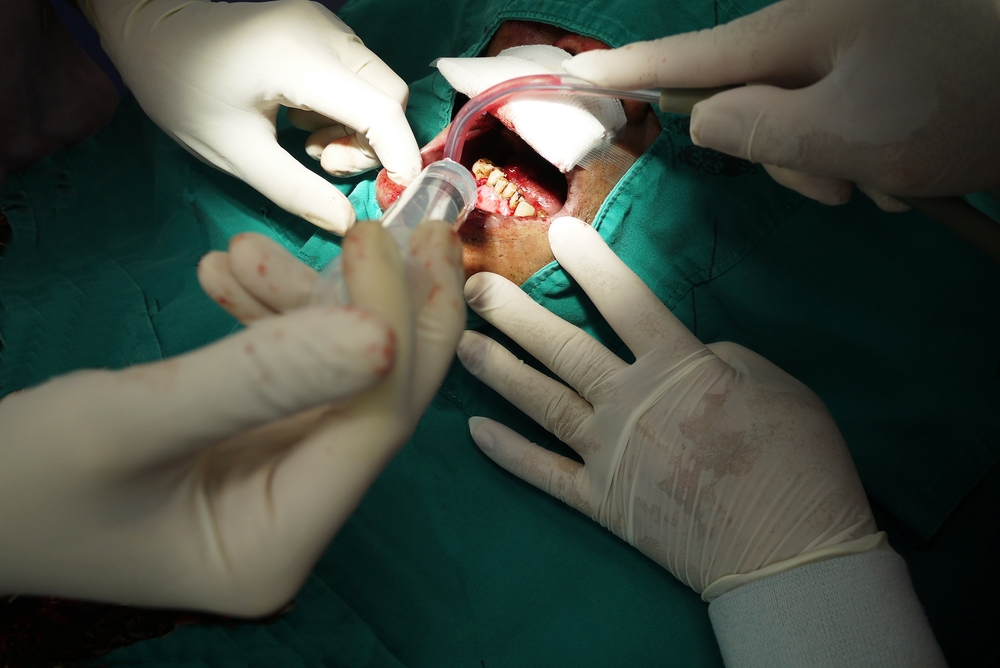
The primary treatment for most oral cancers, surgery involves removing the tumour and some surrounding tissue to ensure all cancerous cells are eliminated.
Radiation therapy
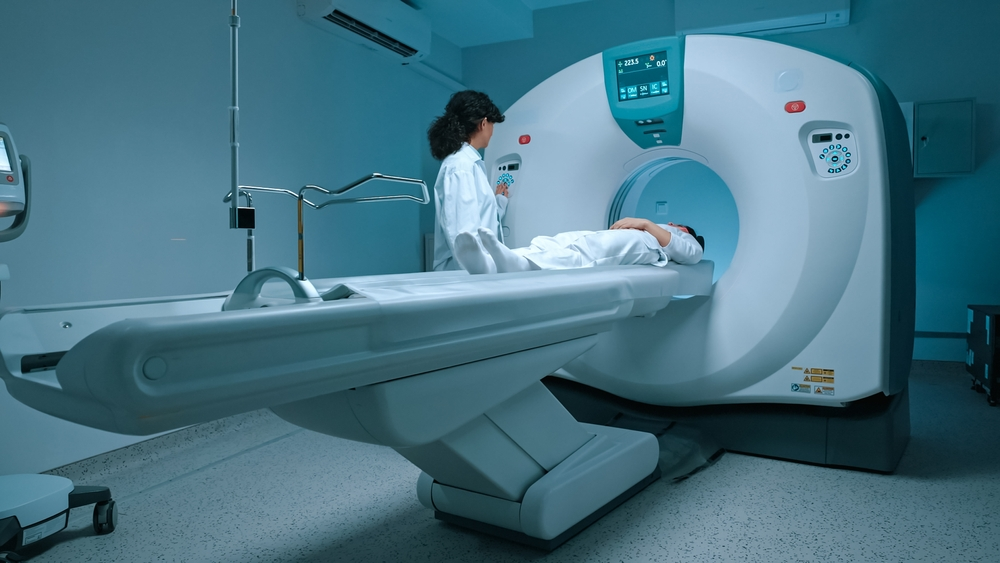
This treatment uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. It is often combined with surgery or chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy

Chemotherapy drugs are used to kill cancer cells and are usually employed in advanced stages or when surgery is not an option.
- Targeted therapy: These drugs attack specific cancer cells without damaging healthy tissue. They are used alongside other treatments to improve outcomes.
Advancements in minimally invasive surgery techniques, such as those pioneered by Dr. Sandeep Nayak, offer better outcomes with reduced recovery times.
Prevention and Early Detection

- Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Use lip balm with SPF to protect your lips from the sun.
- Get vaccinated against HPV.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups and ask your dentist to screen for oral cancer.
Early detection through self-exams and professional screenings significantly improves the chances of successful treatment.
Conclusion
Oral cancer is a serious health condition that requires prompt attention and early detection for better treatment outcomes. Advances in surgical techniques, especially those led by experts like Dr. Sandeep Nayak, have improved survival rates and recovery times. Regular screening, awareness of symptoms, and lifestyle modifications can help in both prevention and early detection.
Support
At MACS Clinic, we are committed to providing world-class care to our patients. Whether you’re local or travelling from abroad, we streamline the process to ensure a single, well-coordinated visit for diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care. Postoperative care can often be managed through telemedicine, making it more convenient for international patients. Trust us to provide the compassionate care you deserve.
FAQs
What are the early signs of oral cancer?
Early signs of oral cancer include persistent mouth sores, red or white patches, unexplained mouth bleeding, and a lump in the neck or mouth.
How is oral cancer treated?
Treatment for oral cancer may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy, depending on the cancer’s stage and location.
Can HPV cause oral cancer?
Yes, HPV, particularly strain HPV-16, is a known risk factor for cancers of the oropharynx, which includes parts of the mouth and throat.
How can I prevent oral cancer?
Preventative measures include quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, protecting your lips from the sun, and getting vaccinated against HPV. Regular dental checkups are also important for early detection.
