Understanding Lip Cancer
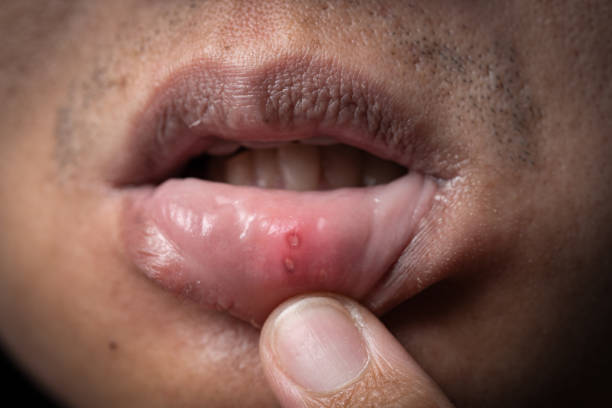
What is Lip Cancer?
Lip cancer is one of the most common types of oral cancer, accounting for nearly one-third of all oral malignancies. It usually affects the lower lip, where the skin is thinner and more exposed to external factors. The cancer begins when abnormal cells multiply uncontrollably, leading to sores, lumps, or persistent changes in the lip’s appearance. If not treated in time, it can spread to the mouth, jaw, and lymph nodes.
At MACS Clinic, experts in head and neck surgery in Bangalore use advanced techniques to diagnose and treat lip cancer effectively.
“A sore on the lip that doesn’t heal is often more than just a wound. Early detection gives the best chance for successful treatment.” – MACS Clinic Team.
Regular checkups and awareness of early symptoms can help in timely intervention and better outcomes.
Worried about a sore on your lip? Here are the signs to watch for.
Symptoms of Lip Cancer
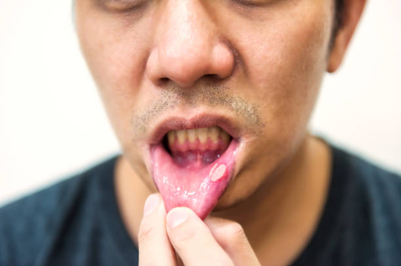
Need Assistance?
If you notice any symptoms or have concerns, seeking a professional evaluation can make a significant difference.
Recognizing the risk factors can help you take action. Here’s what to keep in mind.
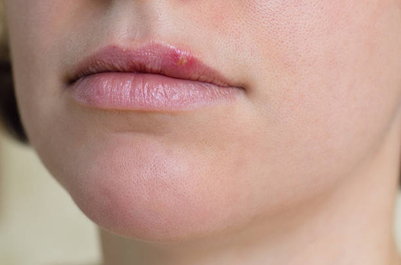
Causes and Risk Factors of Lip Cancer
Tobacco use – Smoking or chewing tobacco damages lip cells.
Excessive sun exposure – UV rays harm the lips, especially the lower lip.
Heavy alcohol consumption – Increases cell damage.
Weakened immune system – Reduces the body’s ability to fight cancerous changes.

HPV infection – Some strains of the virus are linked to oral cancers.
Types of Lip Cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) – The most common form, SCC starts in the flat cells lining the lips and mouth.
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) – Less common, BCC often appears on the lower lip and grows slowly.
Melanoma – Though rare in the lip area, melanoma can occur and often appears as a dark or unusual mole.
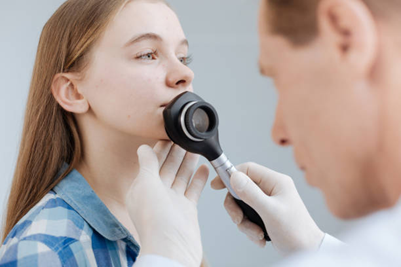
Diagnosing Lip Cancer
Physical Examination: A doctor will check for sores, lumps, or other signs on the lips.
Biopsy: The doctor will remove a small tissue sample from the suspicious area to confirm if it’s cancerous.
Imaging Tests: CT scans, MRIs, PET scans, or X-rays may be used to see if cancer has spread to nearby areas.
Endoscopy: In some cases, an endoscope might be used to examine the mouth and throat for further signs of spread.
Management and Treatment of Lip Cancer
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is the primary treatment for most cases of lip cancer. The goal is to remove the tumor and a margin of healthy tissue around it. More extensive surgery may be needed in advanced stages, which may involve reconstructive procedures to restore lip function and appearance.
Radiation Therapy
Chemotherapy
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
For advanced lip cancer or cases that do not respond to traditional treatments, targeted therapy and immunotherapy are newer, innovative treatments that specifically target cancer cells or stimulate the immune system to fight cancer.
Reconstructive Surgery
After tumor removal, reconstructive surgery may be needed to restore the lip’s appearance and functionality. Depending on the size and location of the tumor, this can include skin grafts or tissue flaps.
Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor for any signs of recurrence. These visits may involve physical exams, imaging tests, and biopsies if necessary.
“Early detection and timely intervention are crucial in successfully treating lip cancer. Advances in surgical techniques, including minimally invasive options, have significantly improved outcomes, making it essential for patients to seek prompt consultation at the first sign of unusual changes in their lips.”
– Dr. Sandeep Nayak, Surgical Oncologist in Bangalore.
Need Assistance?
Stages of Lip Cancer
Stage 0: The tumor is confined to the surface layer of the lip.
Stage I: The cancer is small and limited to the lip, with no spread to lymph nodes.
Stage II: The tumor is larger but still localized.
Stage III: Cancer has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
Stage IV: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body.
Prevention and Risk Reduction
Sun protection: Always use lip balms with SPF and wear hats or scarves to shield the lips from excessive sun exposure.
Avoid smoking and tobacco use: Smoking is a major risk factor for lip cancer. Quitting can lower the risk of developing it.
Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol use can increase the risk of oral cancers, including lip cancer.
Healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables can support oral health and reduce cancer risk.
Regular screenings: Early detection through regular self-exams and professional checkups can catch potential issues early.
FAQs
How common is lip cancer?
Does lip cancer spread quickly?
What are melanoma stages and symptoms?
Is lip cancer fatal?
What is the lip cancer survival rate?
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only and not for promotional use.
