Buccal Mucosa Cancer
Understanding Buccal Mucosa Cancer
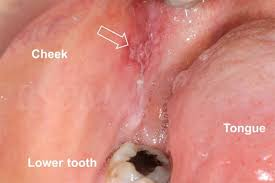
Medical professionals at MACS Clinic, a prominent center for head and neck surgery in Bangalore, highlight the critical role of early detection and prompt treatment.
“Early detection is critical because buccal mucosa cancer can significantly impact functions like speaking, chewing, and swallowing. Identifying the warning signs and seeking timely intervention can make all the difference.”
Symptoms of Buccal Mucosa Cancer
Thickening or swelling in the cheek that causes discomfort
Need Assistance?
If persistent sores or swelling are troubling you, don’t ignore them. Consult a specialist to ensure early detection and proper care.
Diagnosis and Staging
Physical Examination: A detailed inspection of the oral cavity, focusing on the inner cheeks, jaw, and nearby lymph nodes.
Biopsy: A small sample of the affected tissue is taken and analyzed under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancerous cells.
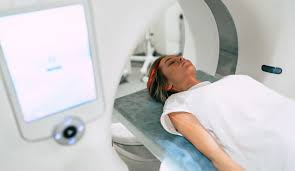
Imaging Tests: Advanced imaging techniques such as CT, MRI, and PET scans help determine the tumor’s size and spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
Staging: Cancer is categorized into stages (I-IV) based on the tumor size, lymph node involvement, and metastasis (spread to distant areas).
Treatment Options for Buccal Mucosa Cancer
Surgery:
Radiation Therapy:
Chemotherapy:
Targeted Therapy:
These treatments target specific cancer cell growth pathways, minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
Need Assistance?
Concerned about unexplained cheek pain? Act now before it’s too late. Seek professional help to address symptoms and maintain your oral health.
Minimally Invasive Approaches
Robotic Surgery for Oral Cancer: Allows surgeons to operate with enhanced precision using robotic arms and 3D imaging. This reduces trauma to surrounding tissues.
Laparoscopic Surgery: Small incisions and specialized tools are used to remove tumors, resulting in less pain, minimal scarring, and faster recovery.
Faster Recovery: Smaller incisions reduce pain, less scarring, and quicker healing.
Precision: Advanced tools allow precise tumor removal, preserving healthy tissues.
Improved Outcomes: Minimally invasive techniques reduce the risk of complications and ensure better patient functional outcomes.
Risk Factors and Prevention of Buccal Cancer
Risk Factors:
Prevention Tips:
Maintain good oral hygiene with regular dental checkups.
Need Assistance?
Are oral ulcers disrupting your life? Get the right guidance for effective treatment and relief. Don’t let delays affect your well-being.
FAQs
Can Buccal Mucosa Cancer spread to other parts of the body?
How long does recovery take after surgery for Buccal Mucosa Cancer?
Recovery time depends on the extent of surgery and overall health. With minimally invasive approaches, most patients recover within 2-4 weeks.
Is Buccal Mucosa Cancer painful?
Can Buccal Mucosa Cancer be prevented?
Who is more prone to Buccal Mucosa Cancer?
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only and not for promotional use.
