Retromolar Trigone Cancer
Retromolar Trigone Cancer – Understanding a rare yet aggressive cancer with expert insights from MACS Clinic in Bangalore. This page provides an in-depth look at retromolar trigone cancer, including its symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic methods, treatment modalities, and the emotional and physical rehabilitation that follows. Our goal is to empower you with knowledge and prepare you for informed discussions with your medical team.
A cancer diagnosis is a life-altering moment. For patients diagnosed with retromolar trigone cancer (RMT cancer), the uncertainty can be even more overwhelming due to the rarity and complexity of the disease. This specific form of head and neck cancer occurs in a small yet critical area behind the last molars, affecting functions like chewing, speaking, and swallowing.
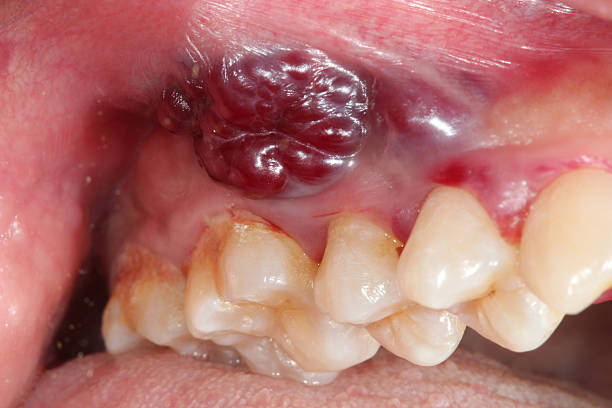
Retromolar trigone cancer requires careful evaluation and a coordinated treatment approach. According to Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a surgical oncologist in Bangalore, “Although rare, retromolar trigone cancer can be aggressive and fast-spreading. With early diagnosis and a carefully tailored treatment plan, outcomes can be significantly improved. Patient awareness and timely intervention are absolutely critical.”
What is Retromolar Trigone Cancer?
The retromolar trigone is a small triangular area located behind the last molar on the lower jaw. Despite its size, its proximity to vital structures like the jawbone, muscles, lymph nodes, and throat makes any cancer in this region potentially dangerous and quick to spread.
RMT cancer is a subtype of oral cancer and is often classified under head and neck cancers. It typically manifests as squamous cell carcinoma, though other variants are possible.
Globally, head and neck cancers account for about 4% of all cancers, and in India, the burden is significantly higher due to the widespread use of tobacco products. India reports over 120,000 new oral cancer cases annually, with a considerable portion involving subsites like the retromolar trigone.
According to MACS Cancer specialists, “While most people haven’t even heard of the retromolar trigone, tumors in this area can silently progress and often go unnoticed until they cause severe pain or dysfunction.”
Need Assistance?
Noticing unexplained pain or swelling behind your molars? Seek professional evaluation to rule out anything serious. Early intervention can change everything.
Symptoms of Retromolar Trigone Cancer
This cancer may not present immediate or obvious symptoms in the early stages. However, certain warning signs should never be ignored. Recognizing the symptoms of RMT cancer early can make a significant difference in survival and quality of life.
Here are common indicators:

“Symptoms may mimic dental problems, leading to misdiagnosis or delayed referrals,” says Dr. Sandeep Nayak. “Dentists and general physicians play a crucial role in recognizing red flags and guiding patients to the right specialists.”
Risk Factors
Like many oral cancers, retromolar trigone cancer has a clear link to lifestyle and environmental exposures. Here’s what increases your risk:
Tobacco Use
Both smoking and chewing tobacco directly irritate the oral mucosa, increasing cellular mutations.
Alcohol Consumption
Especially when combined with tobacco, alcohol acts as a co-carcinogen.

Poor Oral Hygiene
Chronic irritation from ill-fitting dentures or sharp teeth can lead to cellular changes.
Age and Gender
Men over 50 are more commonly affected, though women and younger patients are not immune.
Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of vitamin A and iron may compromise the mucosal barrier.
Dr. Nayak emphasizes, “Preventive education is key. Addressing modifiable risk factors can dramatically reduce the incidence of this preventable cancer.”
Diagnostic Evaluation
Diagnosing retromolar trigone cancer requires a detailed approach, especially since the area is hard to access.
Here’s how doctors evaluate the condition:
Clinical Examination: An ENT or oncologist performs a thorough oral and neck exam.
Biopsy: Tissue sampling is essential for confirming cancer type and grade.
Imaging Studies: CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans help determine the extent of spread, also aiding in retromolar trigone cancer staging.
Endoscopy: Useful for visualizing deeper structures and ruling out additional lesions.
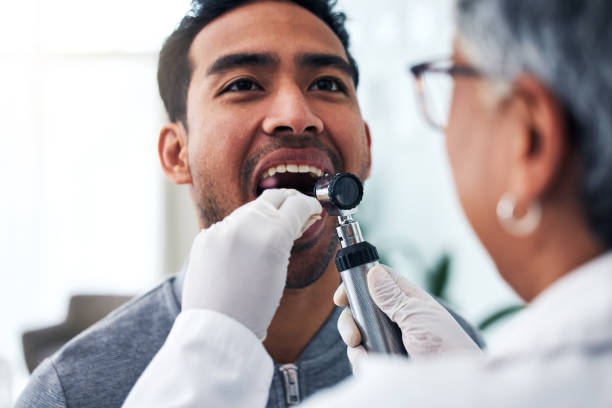
“Accurate staging guides treatment planning. We focus on both local control and systemic safety,” explains Dr. Nayak. “Our diagnostic protocol at MACS Clinic ensures no detail is missed.”
Need Assistance?
Concerned about persistent oral pain or non-healing ulcers? Consult a specialist to understand what’s happening beneath the surface.
Treatment of Retromolar Trigone Cancer
Treatment depends on the stage, tumor size, lymph node involvement, and overall health of the patient. A multi-pronged approach is typically employed, these may include:
Surgical Resection
Often, the first line of treatment involves removing the tumor and surrounding tissues. This may involve retromolar trigone cancer surgery, such as mandibulectomy or neck dissection.
Radiation Therapy
Used either post-operatively or as primary treatment in inoperable cases. Modern techniques like IMRT (Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy) help preserve nearby structures.
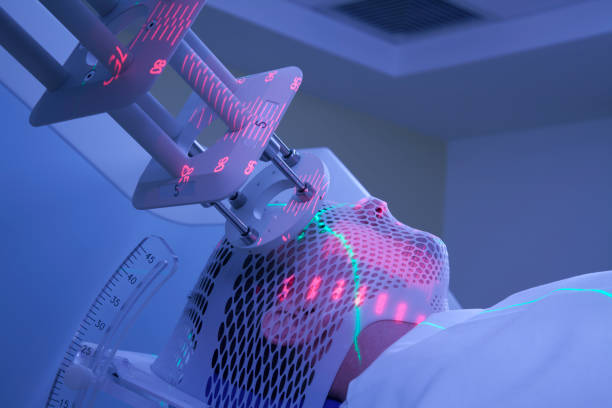
Chemotherapy
Often combined with radiation in advanced cases. Drugs like cisplatin are used to enhance the effect of radiation or shrink tumors pre-surgery.
Targeted Therapy & Immunotherapy
In select cases, targeted agents or immune checkpoint inhibitors may be recommended.
Dr. Sandeep Nayak explains, “Each patient’s treatment is unique. Our goal is to eliminate cancer while preserving critical functions, such as speech and swallowing. Advanced surgical techniques and tailored therapy protocols are essential for this balance.”
Rehabilitation & Support
Recovery after treatment involves not just physical healing, but also emotional and functional restoration.
Supportive care may include:
Speech and Swallow Therapy: Essential after surgery involving oral or jaw structures.
Nutritional Counseling: Maintaining weight and strength during recovery is crucial.
Pain Management: Managing retromolar trigone pain with appropriate medication and support.
Psycho-Oncology Services: Addressing the mental toll of cancer diagnosis and treatment.

“Rehabilitation is as critical as surgery itself,” notes Dr. Nayak. “Our support teams walk with patients long after the surgery is over, because recovery is not linear.”
Need Assistance?
Cancer recovery is about more than just survival. Seek expert guidance to navigate post-treatment life with confidence and dignity.
FAQs
1. How common is retromolar trigone cancer?
2. What is the cause of retromolar trigone cancer?
3. Is retromolar trigone cancer curable?
4. What are the challenges in diagnosing retromolar trigone cancer?
5. Does retromolar trigone cancer affect quality of life?
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only. Individual results may vary. Please consult a qualified doctor for personalized advice
