Understanding Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Hypopharyngeal cancer is a rare and aggressive type of head and neck cancer that begins in the hypopharynx, the lower part of the pharynx, just above the esophagus and behind the voice box. Although it accounts for only about 3–5% of all head and neck cancers, its late detection often makes treatment challenging. In India, hypopharyngeal cancer forms a significant proportion of cancers in individuals with prolonged tobacco and alcohol use, especially in rural regions.
According to Dr. Sandeep Nayak, a leading oncologist in India, “Hypopharyngeal cancer is treatable when detected early. Advancements in minimally invasive surgery and personalized oncology care have transformed outcomes in recent years.”
Dr. Sandeep Nayak is one of the pioneers in advanced laparoscopic and robotic cancer surgeries in India. With decades of experience and numerous accolades, he has treated hundreds of patients with complex head and neck cancers, including hypopharyngeal cancer. His patient-first approach and commitment to precision medicine make him a sought-after expert in this field.
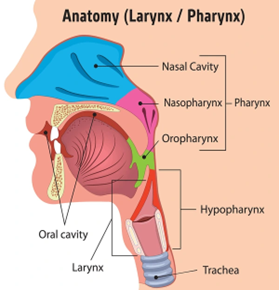
What is Hypopharyngeal Cancer?
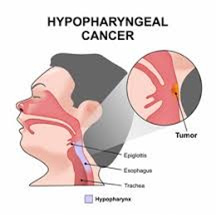
Hypopharyngeal cancer develops in the cells lining the hypopharynx, which plays a vital role in swallowing. Most commonly, it arises as squamous cell carcinoma, affecting the flat cells lining the inner surface. As the cancer grows, it can invade nearby tissues, such as the larynx (voice box) and esophagus, as well as lymph nodes.
This condition is more prevalent in men over 50, especially those with a history of tobacco or alcohol use. Early diagnosis is critical for favorable outcomes, but unfortunately, symptoms often appear late, leading to delayed detection.
Symptoms of Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Hypopharyngeal cancer symptoms often resemble common throat problems, making them easy to overlook. However, persistent or worsening symptoms should always prompt medical evaluation.
Common hypopharyngeal cancer symptoms include:
- Sore throat that doesn’t go away
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Ear pain (especially on one side)
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Lump in the neck (due to lymph node swelling)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent cough
Need Assistance?
Noticing any of these symptoms? Early detection can improve outcomes. Get in touch with a specialist for an accurate diagnosis today.
Causes and Risk Factors of Hypopharyngeal Cancer
The exact cause isn’t always known, but researchers have identified several key risk factors that significantly raise your chances of developing hypopharyngeal cancer.
Top causes and risks include:
Tobacco use – cigarettes, cigars, and especially smokeless tobacco
Excessive alcohol consumption
Nutritional deficiencies, especially low intake of fruits and vegetables
HPV (Human Papillomavirus) infection, particularly in younger individuals
GERD (acid reflux) – long-term irritation can lead to cellular changes
Poor oral hygiene
Occupational exposure to chemicals or asbestos
Types of Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC):
Adenocarcinoma:
Minor Salivary Gland Tumors:
- Pyriform sinus (most common site)
- Posterior pharyngeal wall
- Postcricoid area
Diagnosis of Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Physical Examination:
Endoscopy:
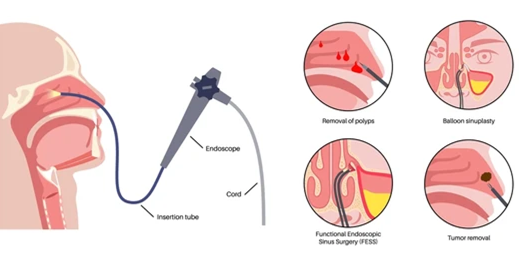
Biopsy:
A tissue sample is taken from a suspicious area and analyzed for cancer cells.
Imaging Tests:
- CT Scan/MRI: These help outline the tumor size, spread, and involvement of surrounding structures.
- PET Scan: This can detect distant metastasis by indicating regions of increased metabolic activity.
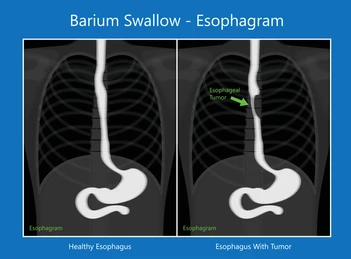
Barium Swallow Test:
Treatment Options for Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Surgery:
- Transoral Robotic Surgery (TORS) or Laser Surgery: For early-stage cancers, these minimally invasive surgeries can remove tumors without large incisions.
- Laryngopharyngectomy: In advanced stages, part or all of the hypopharynx, larynx, and surrounding tissues may need to be removed.
- Neck Dissection: If the cancer has spread to lymph nodes, they may be surgically removed.

Radiation Therapy:
Chemotherapy:

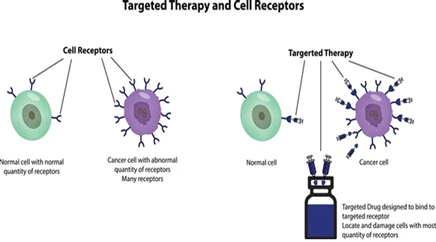
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy:
Rehabilitation:
Prevention and Risk Reduction
While not all cases are preventable, you can significantly lower your risk by adopting healthy habits.
Tips for prevention:
- Avoid tobacco in all forms
- Limit or stop alcohol consumption
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in antioxidants
- Practice good oral hygiene
- Protect against HPV with vaccination and safe practices
- Seek regular screenings if you’re at high risk

Need Assistance?
Looking to lower your risk of hypopharyngeal cancer? Speak with a specialist for guidance on effective prevention strategies.
FAQs
How common is hypopharyngeal cancer?
What are the complications of this condition?
What can I expect if I have hypopharyngeal cancer?
What are hypopharyngeal cancer survival rates?
When should I see a doctor?
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only. Individual results may vary. Please consult a qualified doctor for personalized advice
