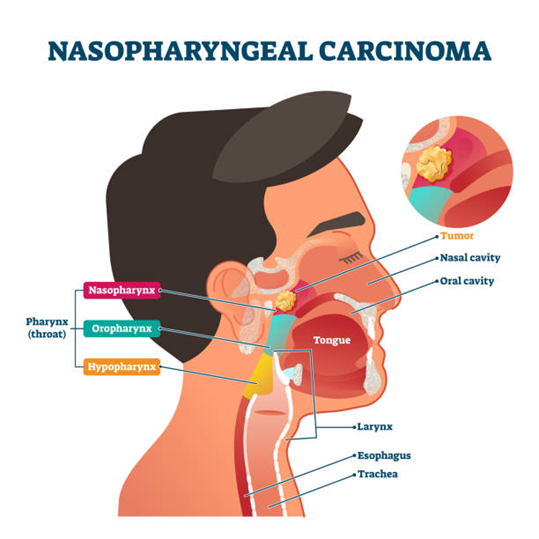
Nasopharyngeal Cancer
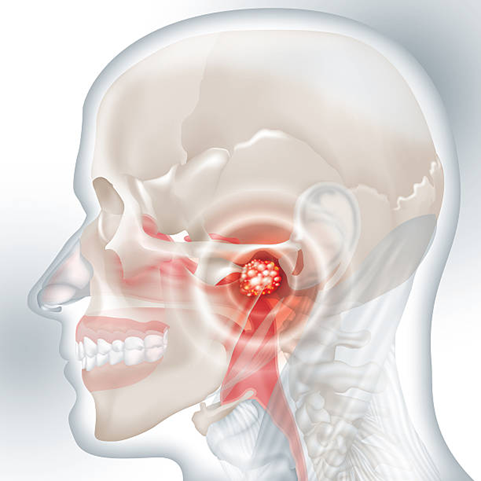
Nasopharyngeal cancer is a rare type of head and neck cancer that develops in the nasopharynx, the upper part of the throat, located behind the nose and above the roof of the mouth. It’s a passageway through which air travels from your nasal passages to your windpipe and lungs. What makes this cancer distinct is its hidden location, which often delays detection until it has already spread to nearby lymph nodes or other areas. Because of this, many patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage, making treatment more complex compared to some other cancers of the head and neck.
Globally, nasopharyngeal cancer represents less than 1% of all cancers, with an incidence of about 1 case per 100,000 people each year. Although uncommon, its clinical behavior and the challenges it poses in diagnosis and treatment make it a subject of growing importance in oncology.
Specialists at MACS Clinic, a trusted centre for nasopharyngeal cancer treatment in Bangalore, emphasize:
“Early detection combined with advanced surgical techniques can significantly improve outcomes, even for deep-seated or complex tumors.”
Types of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Nasopharyngeal cancers are generally classified based on their microscopic appearance.
- Keratinizing Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Rare type, linked to smoking and environmental factors.
- Less responsive to radiation therapy.
- Non-Keratinizing Carcinoma
- More common and strongly associated with Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) infection.
- Subdivided into differentiated and undifferentiated types.
- Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- A rare and aggressive form.
- Often requires a combination of treatments.
Need Assistance?
Experiencing persistent nasal or ear issues? Seek a timely evaluation to rule out severe conditions.
Symptoms of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
The symptoms can be subtle in the early stages, often mimicking common ear, nose, or throat issues. Key warning signs include:
- Persistent nasal congestion or blockage
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Hearing loss or a sensation of fullness in one ear
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Lump in the neck due to enlarged lymph nodes
- Headaches or facial numbness
- Difficulty breathing, speaking, or swallowing
Causes of Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV):
Strongly linked with most cases worldwide.
Genetic predisposition:
A family history increases the risk.
Dietary factors:
High consumption of preserved or salted foods containing nitrosamines may contribute to the risk.
Environmental exposure:
Contact with wood dust, formaldehyde, or other chemicals.
Tobacco and alcohol use:
Increases susceptibility, particularly for keratinizing types.
Understanding these risk factors enables better awareness and the implementation of preventive measures.
Diagnosis and Tests
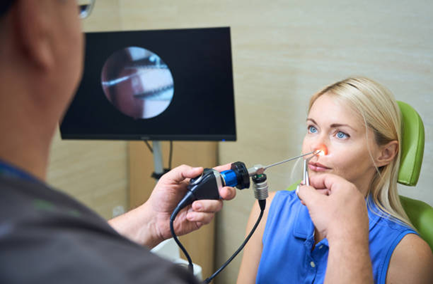
Nasopharyngoscopy:
A thin flexible scope is inserted through the nose to visualize the nasopharynx.
Imaging studies:
Blood tests:
Need Assistance?
If symptoms persist, do not wait—schedule a consultation to discuss safe and effective care.
Management and Treatment
Radiation Therapy
Chemotherapy
Surgery
Surgery is not usually the first line of treatment, but it may be recommended for residual disease after radiation or for recurrent tumors. Different surgical approaches include:
- Endoscopic surgery through the nasal passages for smaller tumors.
- Open surgical procedures are used for larger or more complex cases.
- Neck dissection if lymph nodes are affected.
In select cases, robotic-assisted techniques are employed to access tumors that lie deep within the skull base or beneath the collarbone. At advanced centres such as MACS Clinic, approaches like Transoral Robotic Surgery (TORS) and the Robotic Infraclavicular Approach (RIA) enable surgeons to operate with precision in areas that are otherwise difficult to reach safely.
As Dr. Sandeep Nayak, senior surgical oncologist, notes, “With robotic technology, we are now able to reach tumors in regions once considered inaccessible, offering patients safer procedures and better functional outcomes.”
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
Need Assistance?
Understanding your treatment options can make a difference. Speak with a specialist to explore what’s possible.
FAQs
What are the stages of nasopharyngeal cancer?
Nasopharyngeal cancer is staged from Stage I to Stage IV:
- Stage I: Tumor is small and confined to the nasopharynx.
- Stage II: Tumor grows slightly and may involve nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage III: Larger tumor with more extensive local or lymph node involvement.
- Stage IV: Advanced cancer, spreading to nearby structures or distant organs.
What are the treatment side effects?
Side effects vary depending on therapy:
- Radiation: dry mouth, difficulty swallowing, skin changes.
- Chemotherapy: nausea, fatigue, lowered immunity.
- Surgery: temporary pain, swelling, or speech difficulties.
Most side effects are manageable with supportive care.
Is nasopharyngeal cancer curable?
Yes, especially when detected early. Even in advanced cases, modern treatment techniques can achieve long-term control, reduce the risk of recurrence, and improve survival rates.
Need Assistance?
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only. Individual results may vary. Please consult a qualified doctor for personalized advice
